Mitochondrial metabolites acylcarnitines: therapeutic potential and drug targets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0015Keywords:
acylcarnitine, mitochondrial physiology, energy metabolism, biomarkers, cardiometabolic diseasesAbstract
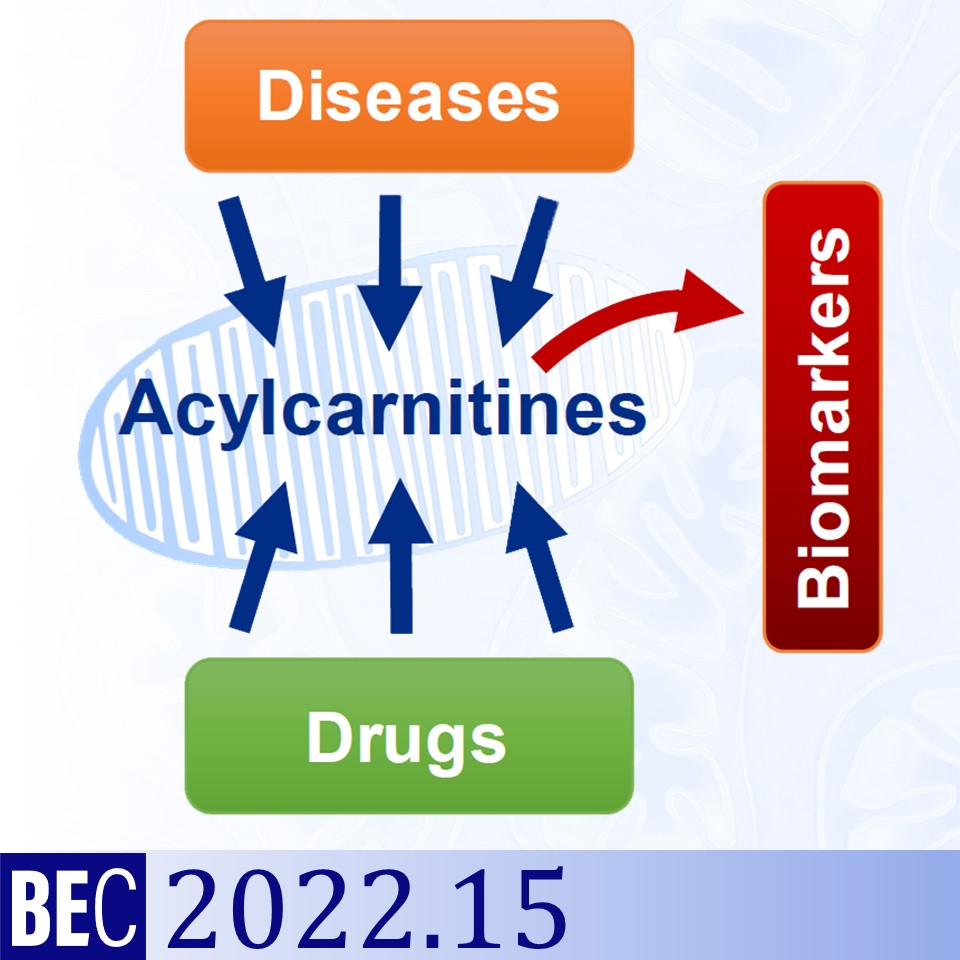
Acylcarnitines are esters of L-carnitine that emerge from the fatty acid metabolism pathways in mitochondria and peroxisomes.
Metabolomic profiling assays that investigate disease and nutrition states often include measurements of different acylcarnitines. This has resulted in increased interest regarding the consequences of increased or decreased plasma acylcarnitine concentrations and the mechanisms associated with these changes. An altered acylcarnitine metabolome is characteristic of specific inborn errors of fatty acid metabolism, and cardiovascular, metabolic, and neurological diseases in addition to some forms of cancer. Long-chain acylcarnitines accumulate under conditions of insufficient mitochondrial functionality reaching tissue levels that can affect enzyme and ion channel activities, and impact energy metabolism pathways and cellular homeostasis.
A better understanding of biochemical and molecular mechanisms behind the changes in acylcarnitine levels and their physiological and pathological roles forms the basis for future therapeutic target selection and preclinical drug discovery. This may explain off-target effects of some clinically used drugs and point to new indications for repurposing.
Cite:
Dambrova M, Cecatto C, Vilskersts R, Liepinsh E (2022) Mitochondrial metabolites acylcarnitines: therapeutic potential and drug targets. Bioenerg Commun 2022.15. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0015
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Maija Dambrova, Cristiane Cecatto, Reinis Vilskersts, Edgars Liepinsh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



